The Basics of Biogas: A Renewable Energy Marvel
Biogas, a powerful player in the realm of alternative energy sources, is revolutionizing how we think about waste and energy production. This renewable energy marvel is not just a solution to our energy needs but also a key to sustainable waste management.
What is Biogas?
Biogas is a mixture of gases produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. This process occurs in the absence of oxygen, where microorganisms break down biodegradable materials, resulting in a combustible gas mixture.
Composition of Biogas
The primary components of biogas include:
- Methane (CH₄): 50-75%
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): 25-45%
- Water Vapor (H₂O): 2-7%
- Trace amounts of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), nitrogen (N₂), and hydrogen (H₂)
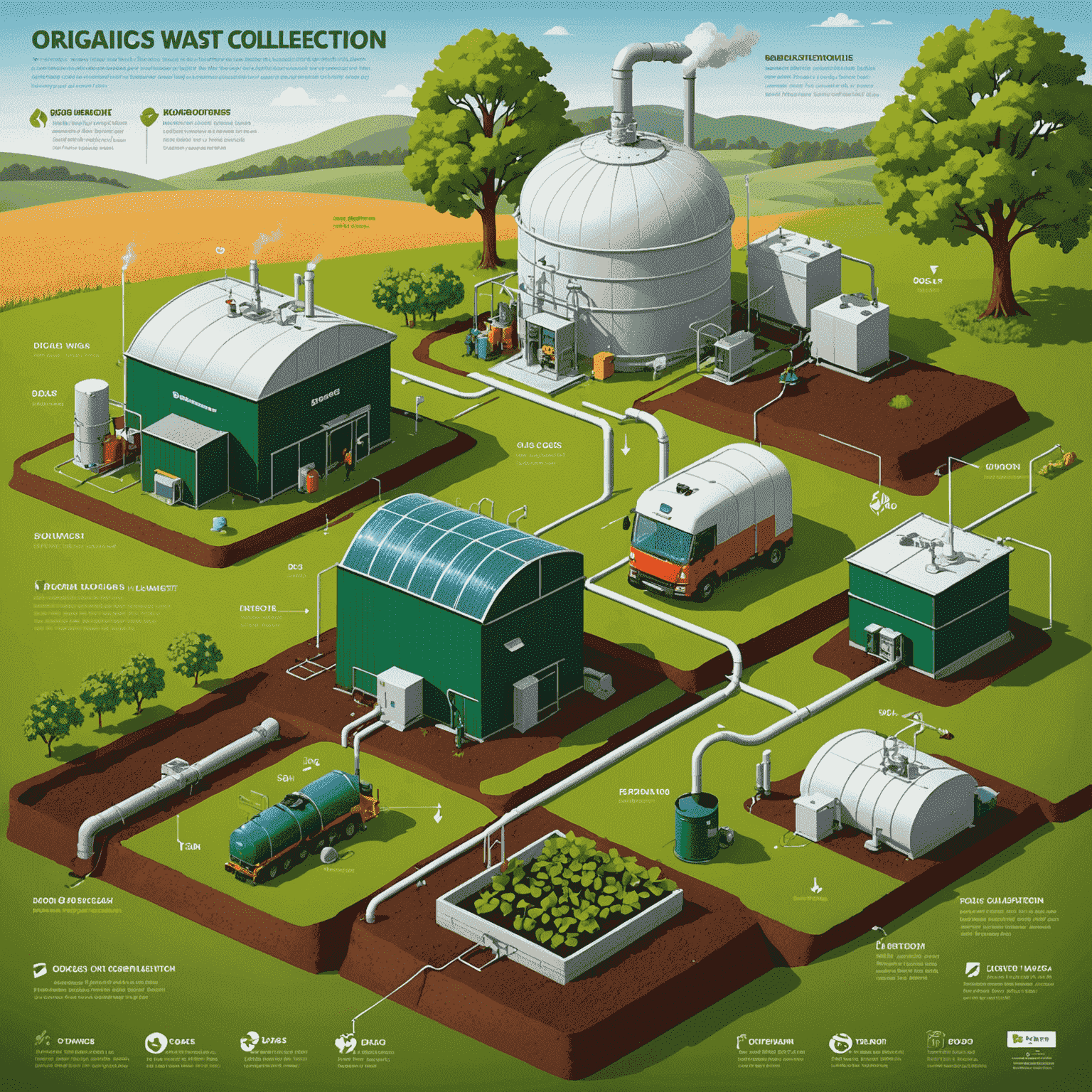
How is Biogas Produced?
Biogas production is a natural process that can be harnessed and optimized in biogas plants. Here's a simplified breakdown of the production process:
- Collection of Organic Waste: This can include agricultural waste, food scraps, sewage, and other biodegradable materials.
- Preprocessing: The organic matter is sorted, ground, and mixed to create a homogeneous substrate.
- Anaerobic Digestion: The prepared organic matter is fed into an airtight container called a digester, where bacteria break down the material in the absence of oxygen.
- Gas Collection: As the bacteria digest the organic matter, they produce biogas, which is collected at the top of the digester.
- Purification: The raw biogas is cleaned to remove impurities, particularly hydrogen sulfide and moisture.
- Utilization: The purified biogas can be used directly for heating or cooking, or it can be further refined into biomethane for use in natural gas vehicles or injection into the gas grid.
The Marvel of Biogas
Biogas is truly a marvel in the world of renewable energy for several reasons:
- Waste Reduction: It provides a solution for organic waste that might otherwise end up in landfills.
- Carbon Neutral: The carbon dioxide released when burning biogas is part of the natural carbon cycle, making it a carbon-neutral fuel source.
- Versatility: Biogas can be used for electricity generation, heating, and as a vehicle fuel.
- Rural Development: Biogas plants can provide energy independence for rural communities, especially in developing countries.
- Fertilizer Production: The digested material left after biogas production is an excellent organic fertilizer.
Conclusion
As we continue to seek sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, biogas stands out as a promising solution. It not only provides clean energy but also addresses waste management issues, making it a true champion in the fight against climate change. By understanding and harnessing the power of biogas, we take a significant step towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.